Introduction to Cold Room and Market Overview
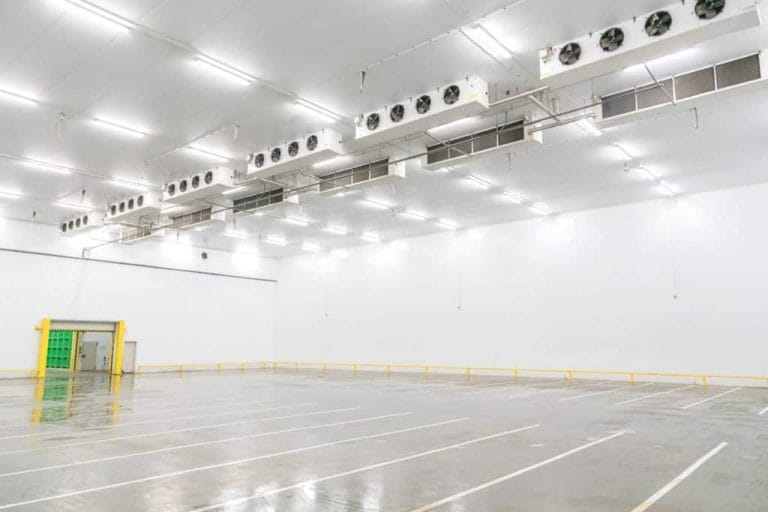
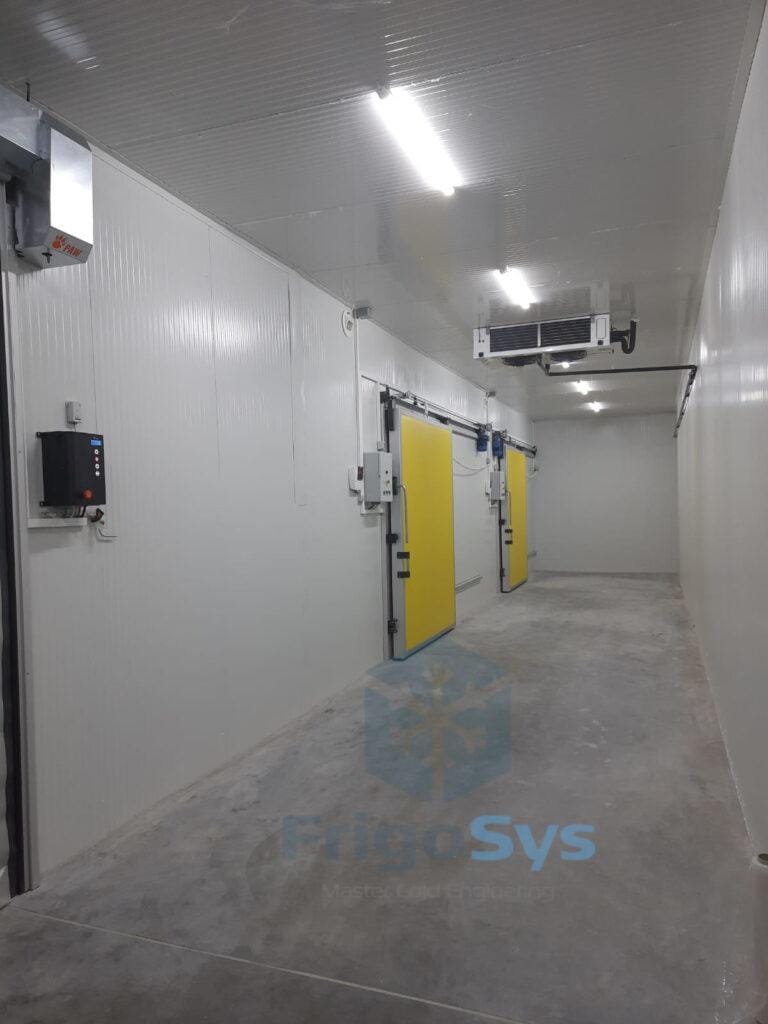
Cold storage is a vital solution for preserving perishables such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. This controlled cooling system extends shelf life and maintains quality standards. The market encompasses diverse options, from modular sandwich panels to complex installations. Growing demand in sectors like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and distribution drives the global cold storage market, reflecting heightened awareness of reducing food wastage and the importance of supply chain efficiency. Investment in technology advancements contributes to an evolving landscape, where energy-efficient and cost-effective solutions are key factors influencing cold room prices.

Fundamental Aspects of Cold Room Economics
- Initial Capital Investment: The costs associated with constructing a cold storage facility include the price of sandwich panels, refrigeration systems, and construction labor.
- Operational Costs: They encompass energy consumption, regular maintenance, and repair of cooling systems to maintain optimal temperatures for stored goods.
- Insulation Efficiency: High-quality sandwich panels reduce the amount of energy required to keep the storage area cold, directly impacting long-term operational expenses.
- Scalability and Flexibility: As demand varies, the ability to expand or modify cold storage space without significant additional investment is economically beneficial.
- Location: Proximity to supply chains and target markets can reduce transportation costs, thereby influencing the overall economic viability of cold storage operations.
Energy Costs: The Leading Component of Cold Room Expenses
Operating a cold storage facility comes with significant expenses, with energy costs being the most prominent. This section’s key points include:
- Electricity Consumption: Cold rooms require continuous energy to maintain low temperatures, leading to high electricity bills.
- Insulation Efficiency: The effectiveness of the insulation directly impacts energy usage; better insulation reduces costs.
- Equipment Efficiency: Up-to-date and properly maintained refrigeration systems consume less power.
- Usage Patterns: Frequent opening of doors and the volume of products stored can influence energy requirements and costs.
Energy considerations are paramount in both the design phase and the daily operation of cold storage facilities.

Real Estate and Location: How Geographical Factors Drive Prices
In the real estate market, location profoundly impacts cold room prices. Geographic factors such as climate, accessibility, and proximity to markets influence the cost of installations and materials like sandwich panels. Here’s how:
- Climate: In areas with extreme temperatures, more robust insulation and cooling systems are mandatory, elevating costs.
- Accessibility: Remote locations can increase transportation expenses for materials and labor, reflected in the final price.
- Proximity to Markets: Being near to urban centers often leads to higher property values and, subsequently, to more expensive installation services.
The Role of Government Regulations and Compliance Costs
Government regulations play a crucial part in determining cold room prices. These regulations are designed to ensure safety, environmental protection, and energy efficiency, which can affect the materials and designs used.
- Safety Standards: Adherence to building codes and safety standards can increase construction costs due to the higher quality materials and installation processes required.
- Environmental Regulations: Eco-friendly refrigerants and insulation with low global warming potential may cost more but are often mandated by law.
- Energy Efficiency: Compliance with energy conservation standards can necessitate advanced technologies that may have higher initial costs but potentially lead to long-term savings.
- Inspection and Certification: The costs for necessary inspections and certifications, which ensure compliance with all regulations, can add to the overall expense.
Businesses must account for these compliance costs when budgeting for cold room installations to avoid unexpected expenses and legal complications.
Scaling Effects: The Relationship Between Size and Price in Cold Room
When it comes to cold storage construction, the size of the facility plays a pivotal role in determining cost. There’s a non-linear scaling effect to consider:
- Economy of Scale: Larger cold storage units typically benefit from economies of scale, meaning the cost per cubic foot decreases as the size increases. Bulk materials purchase and streamlined designs contribute to this effect.
- Complexity Costs: Conversely, as cold rooms grow in size, their complexity can increase. This might involve sophisticated refrigeration systems or advanced insulation techniques, leading to higher costs in design and technology.
- Customization and Small Scale: Smaller units, while less cost-effective in terms of space, may incur additional costs due to the need for customization to fit specific site or operational requirements.
- Operational Efficiency: Larger facilities may also yield operational efficiencies that can offset higher upfront costs with savings in long-term operations.
It’s essential to balance these factors when planning a cold storage investment.

Operational Costs: Labor and Maintenance Overheads
When assessing cold room prices, it’s crucial to consider operational costs. Two significant overheads are:
- Labor: Cold rooms require regular monitoring, restocking, and cleaning. Payroll expenses for staff handling these tasks can impact the total cost of operation.
- Maintenance: Ensuring the longevity of a cold room necessitates ongoing maintenance. This includes:
- Routine inspections
- Cleaning of evaporator and condenser coils
- Checking and replacing worn seals and gaskets
- Upkeep of refrigeration units to prevent system failures
Failure to maintain the cold room can lead to increased energy consumption and potential spoilage of stored goods, thereby inflating operational costs.
The Influence of Construction and Insulation Materials on Price
When assessing cold room prices, the materials used for construction and insulation are pivotal price determinants. For the structural components, the expense varies with the choice between pre-fabricated sandwich panels, which are cost-effective, and custom-built alternatives, which might be pricier but tailored to specific needs. Insulation materials also range widely, from standard polyurethane foam (PUF) to advanced polystyrene or vacuum-insulated panels, with the higher-grade insulators commanding a premium. Additionally, the thickness of these materials directly correlates to both thermal efficiency and cost, influencing the overall investment in a cold storage facility. Hence, selecting the right balance between material quality and expense is crucial for budget management in cold room installations.
Market Demand Trends: Seasonal Variability and Its Consequences
Market demand for cold rooms fluctuates seasonally, impacting prices significantly. During peak seasons, such as summer for perishable goods storage, demand surges, causing prices to rise due to increased competition for cold storage solutions. Conversely, off-peak seasons may see reduced demand, potentially leading to lower prices to attract buyers. This cyclicality can affect:
- Budgeting and Procurement: Companies must anticipate seasonal price changes to optimize purchasing strategies.
- Installation Schedules: High demand periods might lead to longer wait times for installation, disrupting business operations.
- Inventory Management: Seasonal variability necessitates strategic stock management to ensure sufficient storage is available when needed.
- Market Entry Timing: New entrants must consider these trends to time their market entry for competitive pricing and availability.
Recognizing these patterns is crucial for stakeholders to mitigate the consequences of seasonal variability in cold room prices.
Future Outlook: Forecasting Cold Room Cost Trends and Innovations
As the global market evolves, cold storage costs are anticipated to reflect several key trends and innovations:
- Sustainable Technologies: Emphasis on eco-friendly refrigerants and energy-efficient insulation will grow, potentially increasing initial costs but offering long-term savings.
- Automation and IoT: The integration of automation and the Internet of Things (IoT) is expected to enhance efficiency but could also drive up installation costs.
- Scalable Designs: Modular and scalable facilities will become more common, allowing for cost-effective expansion.
- Government Regulations: Stricter regulations may lead to additional compliance costs.
- Economies of Scale: Increased demand for cold storage solutions may lower costs through economies of scale.
These evolving elements are likely to shape the financial landscape of cold room investments, promising both challenges and advancements.
You can contact us to get a cold room price quote.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Cold Room Price
The diversity in cold storage pricing reflects the myriad of factors influencing cost, from the choice of sandwich panels to the intricacies of full installations. Businesses must assess their specific needs against the backdrop of evolving technologies, energy efficiency standards, and market dynamics. Moreover, long-term operational expenses, such as maintenance and energy consumption, should be carefully considered alongside initial outlays. Navigating this complex landscape requires thorough research, clear prioritization, and, ideally, guidance from industry experts to ensure the investment aligns with both budgetary constraints and operational aspirations.